
Priority Sectors for Investment
Priority Sectors for Investment
Agriculture
Aimed at modernizing and increasing productivity of the sector through the following actions:
- Increased Food Security activities;
- Transformation from Subsistent to Commercial Agriculture including development of agricultural chains and market promotion;
- Increased Production and Productivity.
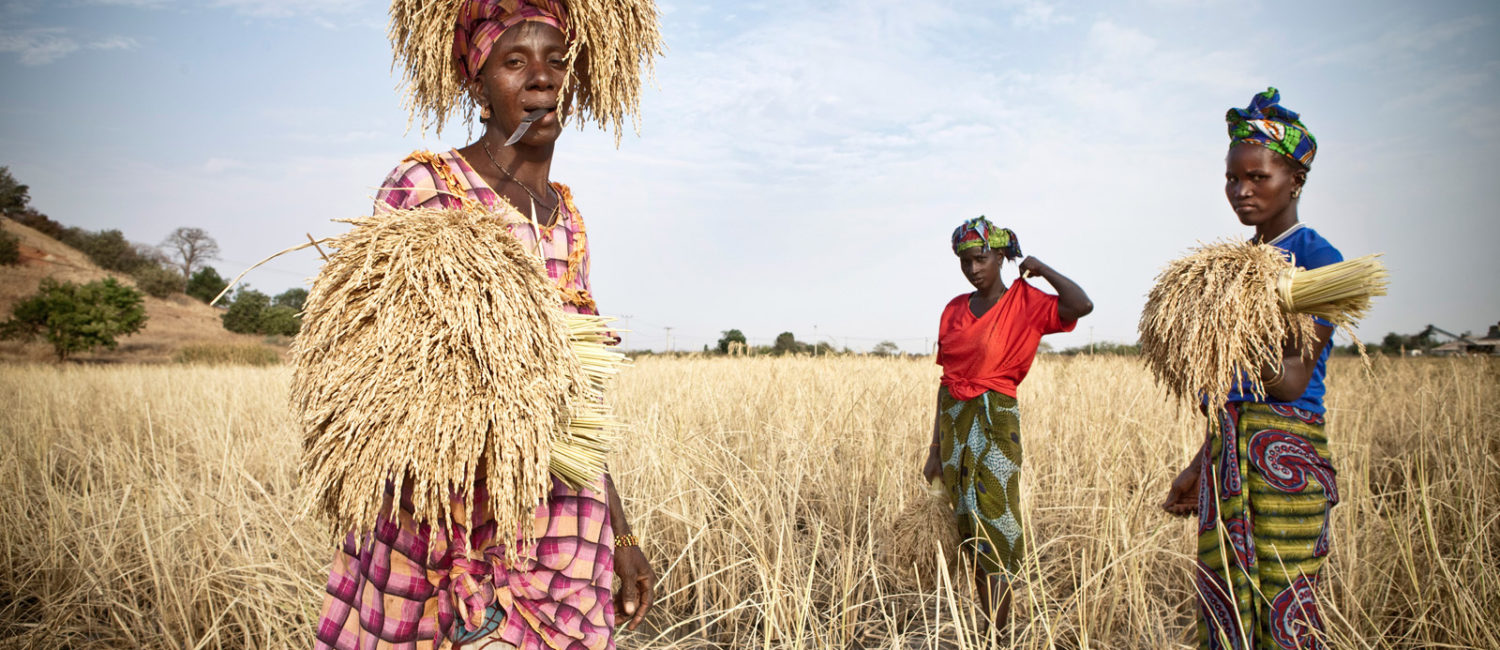
Agriculture is the most important sector in the Gambian economy. The country has over 480,000 hectares of good quality arable land, of which an estimated 180,000 hectares is currently under cultivation. With abundant land, favourable climate, rich soils, relatively low labour cost and close proximity to Western markets, The Gambia offers good opportunities for investment in the agricultural sector. These are complemented by the availability of outlets in the expanding tourism industry, the large concentration of consumers in the urban areas and the ever growing export markets, which provide ample opportunities for investment in the sector, including:
- Crop production and processing (Rice, Maize, Millet, Sorghum, Groundnuts, Sesame, and Cashew)
- Horticulture production and processing (fruits and vegetables)
- Floriculture
- Poultry production
- Livestock production and processing
- Increased passenger air links, both direct to Europe and the USA, but also to regional hubs.
- Air cargo services
- Airport services
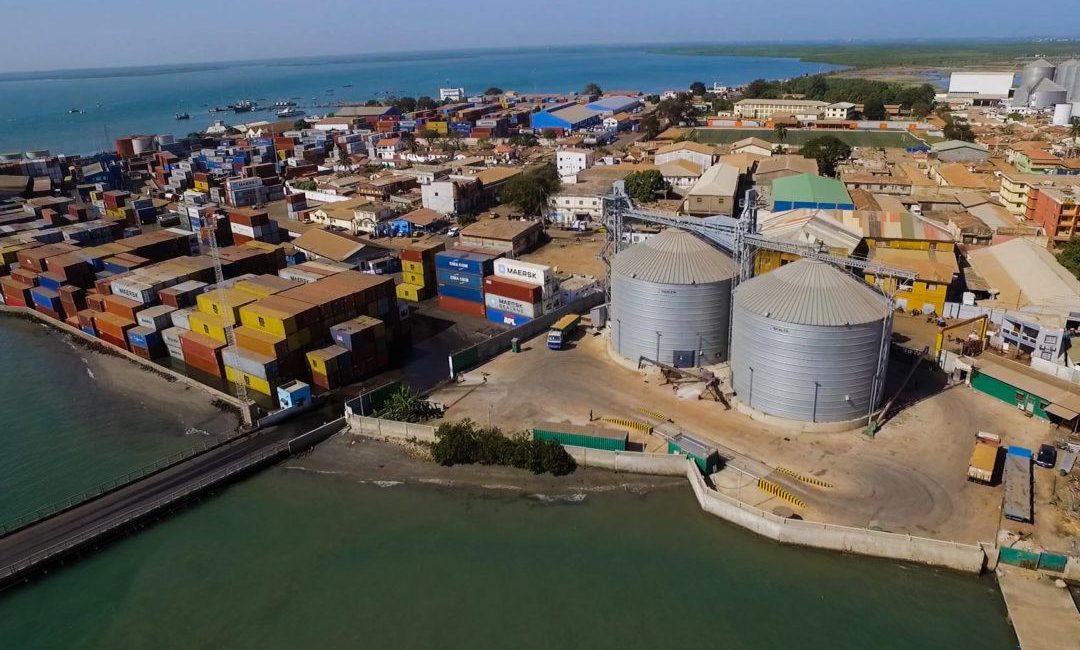
- Sea cargo services, both for The Gambia and transhipment to regional markets
- Food and drink processing and packaging
- Machinery manufacturing and servicing (particularly for the agriculture, food and fisheries industries)
- Plastics for the consumer market, and for the construction industry
- Stainless steel fabrication
- Basic electronics assembly
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing or packaging
- Healthcare products (complimentary medicines, medical devices etc.)
- Pelagic Species: Bonga, sardinella, red mullet, shads, catfish, jacks and snapper.
- Currently frozen shrimps and prawns account for over one third of all fish exports.CosmeticsRiver transportation both for cargo, passengers and tourists.
- Animal feed production
- Agro-processing and packaging
- Machinery manufacturing and servicing
- Provision of cold storage and silos facilities for horticulture and livestock products
- Establishment of Financing Facilities e.g. an Agricultural Development Bank to increase access to financing in the sector.
- Demersal Species: Sole, grunts, seabreams, carangids and cephalopods.

Species:
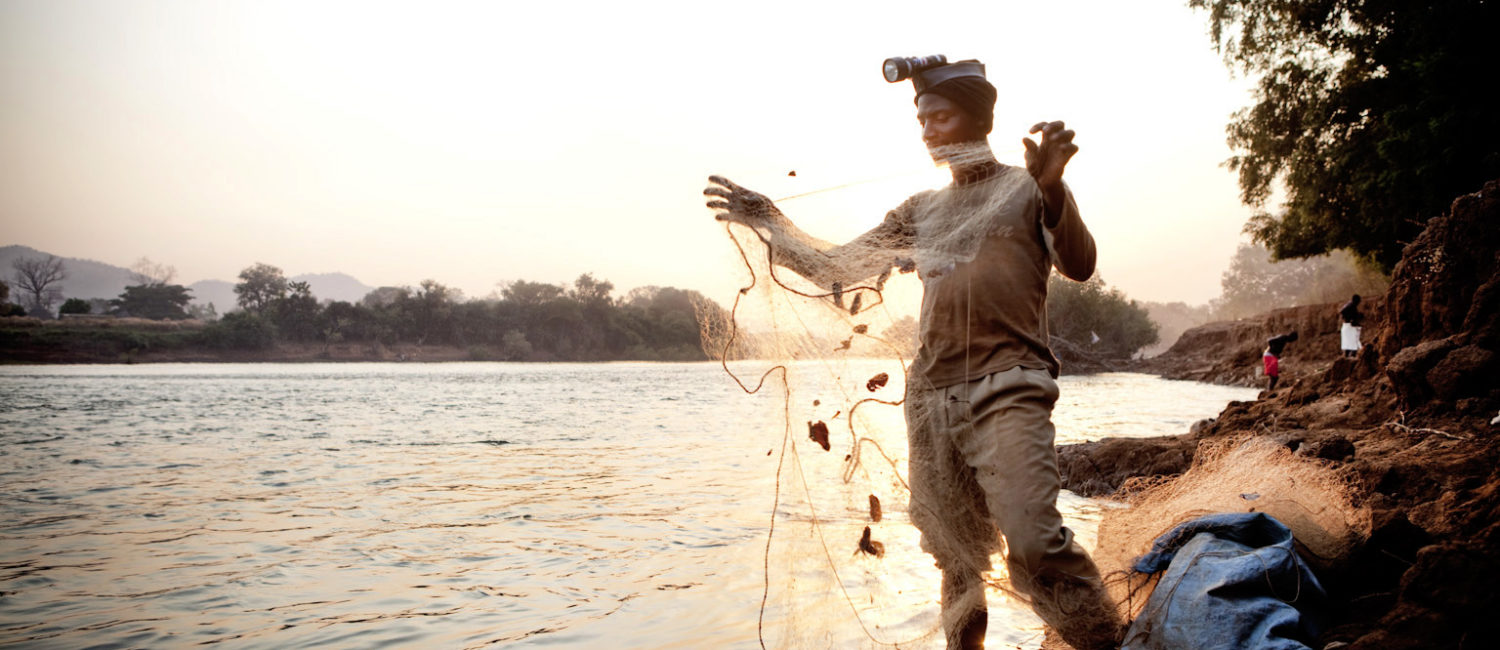
There exist immediate opportunities for vessel operator/traders to supply the existing processing plants with fish, either by supplying fish under contract, or on some form of joint venture basis with the plants. There are also longer term opportunities for companies with an established market presence to source products, either raw or processed from The Gambia.
Fisheries:
The fisheries sector has significant potential for further development in The Gambia. Although it has a coastline of only 80 Kms, The Gambia’s waters can be fished year round and are relatively well populated by a wide variety of demersal and pelagic fish and crustaceans. Total annual fish production in 2002 was circa 43,000 metric tonnes (mt), of which only 573 tonnes was exported in 2003. Most exports are aimed at EU markets. It is believed that the Maximum Sustainable Yield for all species in Gambian territorial waters stands at between 150,000 mt. and 200,000 mt.

Tourism:
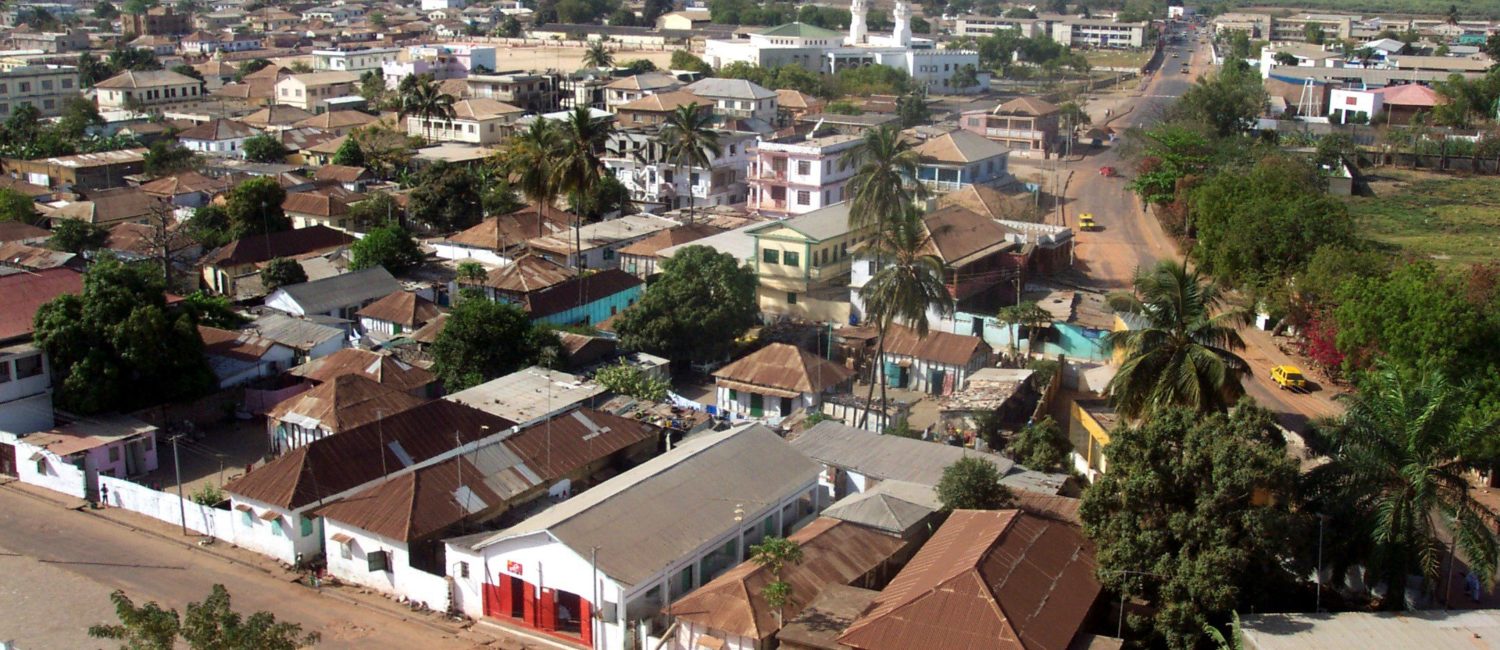
Tourism is one of The Gambia’s fastest growing industries, contributing about 16% of GDP and constituting the largest source of formal non-farm employment. Every year tens of thousands of holidaymakers visit The Gambia from various parts of the world.
The Gambia has excellent potential for further tourism development due to the ease with which it can be reached from the main European markets, the relatively good value for money offered by package tours to the country and its distinctive advantages. These include a favourable climate, excellent beaches, an unspoiled countryside, an agreeable ambience, and above all, a friendly and hospitable population.
Present policy focus in the industry emphasizes the up-market approach, which seeks increased investor participation in five-star hotel projects and quality service apartments. Consolidating and refurbishing the Tourism Development Area (TDA) along the wide Atlantic coast especially reserved for top-of-the market hotel projects, continues to be a major policy thrust to develop tourism in The Gambia. The ease of transportation on the Kombo coastal road covering the entire TDA, the continuous enhancement of electricity supply and telecommunication extensions in the TDA, and the setting up of the Gambia Tourism Board as an independent body to coordinate all aspects of project implementation in, and development of the tourism industry, including, importantly, the grading and classifying of hotels and related resorts, all represent a systematic effort at improving the enabling environment for increased private sector investment in the industry.

Information & Communications Technology:
Harness ICT as a tool to foster growth and employment through modernisation and expansion of the existing telecommunication infrastructure as well as increasing the Country’s Bandwidth.
River and Air Transportation:
Opportunities exist in this sector to improve existing services, add new services or provide services not currently available, including transportation along the Gambia river.
The Port of Banjul is the major port in The Gambia and is one of the most efficient and safest in the region. Its location, 26 miles from the Atlantic Ocean on the Gambia River, allows access to both ocean going vessels and smaller vessels which can navigate up to 300 miles into the interior (the Gambia river).

Health:
- Sustaining gains registered in immunization coverage
- Reducing infant and maternal mortality.
- Combating the problems of HIV/AIDS, Malaria and other diseases through the strengthening of the primary, secondary and tertiary health care.
Education:
Interventions in education will focus on enhancing the Human Capital base of the country through improving access and quality at all levels of Education and linking skills to the job market.
Mining:
The Gambia does not have large discovered deposits of precious minerals or gems, but there are deposits of lower value minerals in certain areas. Successful mining of sand for valuable minerals is taking place near the coast South of Banjul, in a high amenity area under strict environmental control. Opportunities exist initially in exploration for minerals and oil and gas, and the Government of The Gambia is very supportive of these efforts.
Manufacturing:
The Gambia’s manufacturing sector continues to be under developed with a limited manufacturing base focused mainly at the domestic market, and utilizing a limited range of skills and technology. The Government’s strategy is to build on the small domestic base to encourage companies to supply the Gambian and regional markets, and subsequently develop products which can be exported to the EU and the US. Particular opportunities exist in the following areas.

Energy:
Due to the rapid growth in the population of The Gambia in recent years, demand for energy has far outstripped the ability of the State owned utility, NAWEC, to supply.
The provision of reliable electricity to The Gambia has become a priority for the Government and there are opportunities at all levels. Generation capacity is substantially below demand, and particularly with the development of industry and tourism upcountry, opportunities will arise there also. The distribution system, while adequate for existing generating levels will also need investment.
Investment will be geared towards provision of aadequate, affordable and reliable energy supply to support socio-economic development. Strategies envisaged will include: increasing generation, transmission and distribution capacities; exploiting renewable energy potentials and improving energy efficiency.



Contact
The Gambia High Commission in Senegal-Dakar
Villa No. 128, Cite des Jeunes Cadres – Yoff Toundoup Rya, B.P 3248 Dakar, Republic of Senegal
Official Email: gambiaembassydakar@gmail.com
Official Telephone Contact : (+221) 33 820 11 98
Fax: (+221) 33 820 10 56
Official working hours
Monday – Thursday: 09:00hrs – 16:00hrs
Friday: 09:00hrs – 12:30hrs
Saturday, Sunday and Holidays: Closed
